Question 1
> f:=x->x^3*exp(3*x)*cos(2*x);
![]()
> a1:=(D@@3)(f)(1);
![]()
> a2:=evalf(a1);
![]()
Question 2
> restart;
> f:=x->x^3*exp(3*x)*cos(2*x);
![]()
> a1:=int(f(x),x=0..1);
![]()
> a2:=evalf(a1);
![]()
Question 3
> restart;
> g(x):=exp(a*x)*cos(b*x);
![]()
> a1:=taylor(g(x),x=0,8);
![]()
![]()
> a2:=op(15,a1);
![]()
Question 4
> a3:=subs(a=cos(Pi/14),b=sin(Pi/14),a2);
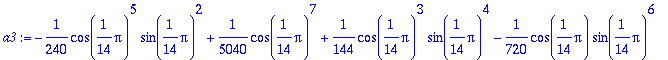
> combine(a3);
![]()
Question 5
> restart;
> f:=(exp(x)-exp(sin(x)))/x^3;
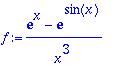
> limit(f,x=0);
![]()
Question 6
> h:=x->2-cos(x)+sin(x)-exp(x);
![]()
> Digits:=10; h(10.0^(-10));
![]()
![]()
> Digits:=20; h(10.0^(-10));
![]()
![]()
> Digits:=30; h(10.0^(-10));
![]()
![]()
> Digits:=40; h(10.0^(-10));
![]()
![]()
> Digits:=50; h(10.0^(-10));
![]()
![]()
> Digits:=60; h(10.0^(-10));
![]()
![]()
Question 7
> restart;
> fsolve(x^5-x-1/2=0);
![]()
Question 8
> restart;
> with(linalg):
Warning, the protected names norm and trace have been redefined and unprotected
> A:=matrix(4,4,[2.0,0,-1,1,0,2,0,1,0,-2,2,-2,2,-1,0,1]);
![A := matrix([[2.0, 0, -1, 1], [0, 2, 0, 1], [0, -2,...](examan/examan29.gif)
> ev:=eigenvects(A);
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
> ev[4][1];ev[4][3][1];
![]()
![]()
Question 9
> restart; with(linalg):
Warning, the protected names norm and trace have been redefined and unprotected
> A:=matrix(3,3,[a,1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]);
![A := matrix([[a, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]])](examan/examan38.gif)
> ev:=eigenvals(A);
![]()
> expand(ev[2]*ev[3]);
![]()
Question 10
> restart; with(linalg):
Warning, the protected names norm and trace have been redefined and unprotected
> v:=vector([sqrt(t)*cos(t),sqrt(t)*sin(t),t]);
![]()
> w:=map(p->diff(p,t),v);
![]()
> am:=dotprod(w,w,orthogonal);
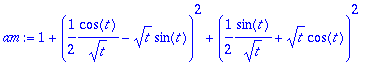
> an:=factor(simplify(am));

> sqrt(an);

=====================================================================
Question 1
> restart;
> f1:=x->sin(x) ; f2:=x->c*x*exp(-x);
![]()
![]()
> e1:= f1(a)=f2(a); e2:= D(f1)(a)=D(f2)(a);
![]()
![]()
> subs(c=solve(e1,c),e2);
![]()
> plot({cot(a),1/a-1},a=0..2*Pi,-4..4,discont=true);
![[Maple Plot]](examan/examan51.gif)
> plot({cot(a),1/a-1},a=0..0.4,-4..40,discont=true);
![[Maple Plot]](examan/examan52.gif)
> sol1:=fsolve({e1,e2},{a,c},a=1..3);
![]()
> sol2:=fsolve({e1,e2},{a,c},a=4..6);
![]()
> f:=piecewise(x<a,f1(x),f2(x));
![f := PIECEWISE([sin(x), x < a],[c*x*exp(-x), otherw...](examan/examan55.gif)
> plot(subs(sol1,f),x=-10..20);
![[Maple Plot]](examan/examan56.gif)
> plot(subs(sol2,f),x=-10..20);
![[Maple Plot]](examan/examan57.gif)
Question 2
> restart;
> with(linalg):
Warning, the protected names norm and trace have been redefined and unprotected
> B:=matrix(3,3,[1,2,-2*s,6+s,3,1,1,-1,2]);
![B := matrix([[1, 2, -2*s], [6+s, 3, 1], [1, -1, 2]]...](examan/examan58.gif)
> p1:=charpoly(B,lambda);
![]()
> p2:=diff(p1,lambda);
![]()
B has two eqaul eigenvalues when if lambda=0 or 4. What does this mean for s?
> s1:=solve( subs(lambda=0,p1), s);
![]()
> s2:=solve( subs(lambda=4,p1), s);
![]()
> eigenvects( map( p->subs(s=s1[1],p) , B) );
![]()
> eigenvects( map( p->subs(s=s1[2],p) , B) );
![]()
> eigenvects( map( p->subs(s=s2[1],p) , B) );
![]()
> eigenvects( map( p->subs(s=s2[2],p) , B) );
![]()
The geometric multiplicity is always 1, even for the eigenvalue with algebraic multiplicity 2.
>
Question 3
> restart;
> Digits:=1005;
![]()
> p:=evalf(sin(1));
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
> for i from 1 to 1000 do p:=p*10: d[i]:=floor(p): p:=p-d[i]: od:
>
> for n from 0 to 9 do
>
q[n]:=0:
> for j from 1 to 1000 do if(d[j]=n) then q[n]:=q[n]+1 fi: od:
> print(q[n]); od:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Question 4
> restart;
> with(plots):
Warning, the name changecoords has been redefined
> implicitplot(x^4+y^4=1,x=-1.5..1.5,y=-1.5..1.5);
![[Maple Plot]](examan/examan88.gif)
> implicitplot(x^2+y^2=4/3,x=-1.5..1.5,y=-1.5..1.5);
![[Maple Plot]](examan/examan89.gif)
> implicitplot({x^2+y^2=4/3,x^4+y^4=1},x=-1.5..1.5,y=-1.5..1.5);
![[Maple Plot]](examan/examan90.gif)
> sol1:=fsolve({x^2+y^2=4/3,x^4+y^4=1},{x,y},x=-0.8..1,y=0.5..0.8);
![]()
> sol2:=fsolve({x^2+y^2=4/3,x^4+y^4=1},{x,y},y=-0.8..1,x=0.5..0.8);
![]()
I am not expecting the students to do the next bit......
If we work in polar coordinates r,theta we have r^2=4/3 and r^4 (sin^4 theta + cos^4 theta) = 1. So r = sqrt(4/3) and
sin^4 theta + cos^4 theta = 9/16. so (1-cos^2 theta)^2 + cos^4 theta = 9/16. Let's find cos theta:
> ct:=solve((1-c^2)^2+c^4=9/16 , c);
![]()
For each value of cos theta there are two values of sin theta. So we get 8 points. For example
> c:=1/4*sqrt(8+2*sqrt(2)): pt:=( sqrt(4/3)*c, sqrt(4/3)*sqrt(1-c^2));
![]()
> evalf(pt);
![]()
> I1:=int((1-x^4)^(1/4)-(4/3-x^2)^(1/2), x=pt[2]..pt[1]);
> evalf(I1);
==================================================================================================
>